Types of Routing in ASP.NET Web App | Custom Routing in ASP.NET
Table of contents
What is routing?
Routing in ASP.NET refers to the mechanism by which URLs are mapped to specific resources or controllers in your web application. It allows you to define URL patterns and associate them with specific actions or handlers in your application.
The default URL of the site or app is defined in Program.cs file, which maps the url to the particular controller and its method.
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
Let's decode the code
app: This refers to an instance ofIApplicationBuilder, which is the interface that provides mechanisms to configure the application's request pipeline.MapControllerRoute: This method is used to define a route for controller actions. It specifies how incoming requests are mapped to controller classes and their action methods.name: "default": This provides a name for the route. It's useful for referring to this specific route elsewhere in the application, such as generating URLs based on this route.pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}": This parameter defines the URL pattern for the route. It consists of placeholders enclosed in curly braces ({}) that represent dynamic parts of the URL. Here's what each part means:{controller=Home}: This placeholder represents the controller segment of the URL. It defaults toHomeif not specified explicitly in the URL.{action=Index}: This placeholder represents the action segment of the URL, which corresponds to a method within the controller. It defaults toIndexif not specified explicitly in the URL.{id?}: This placeholder represents an optional parameter segment of the URL. The question mark (?) indicates that theidparameter is optional. If provided, it will be passed to the action method. If not provided, the action method can handle the absence of theid.
Types of routing in ASP.NET:
Convention Based Routing
Convention-based mapping simplifies routing configuration by following predictable naming conventions. However, it's important to note that more complex routing requirements may still require explicit route configuration using attributes or additional route definitions.
app.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");Instead of defining the controller route we can also define it as
app.MapDefaultControllerRoute();which routes the request to the HomeController's Index method.Remember: The requested url must match the pattern.
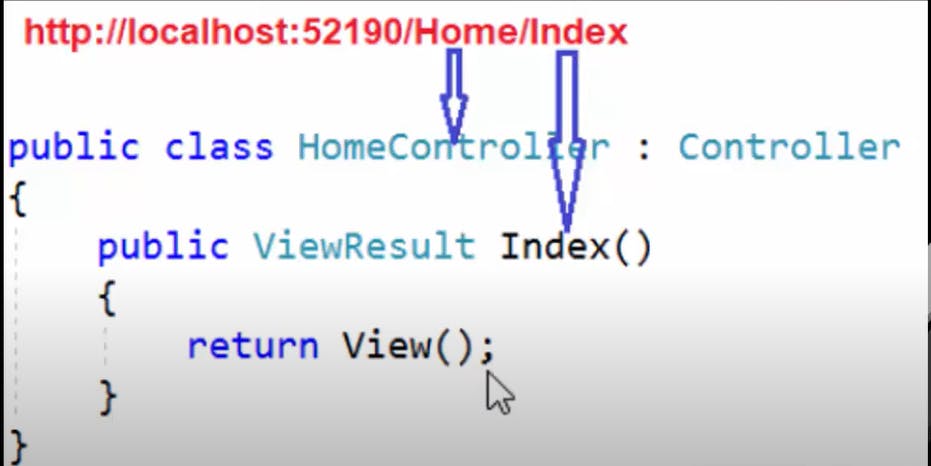
Navigation to custom view/defining custom views using attribute routing
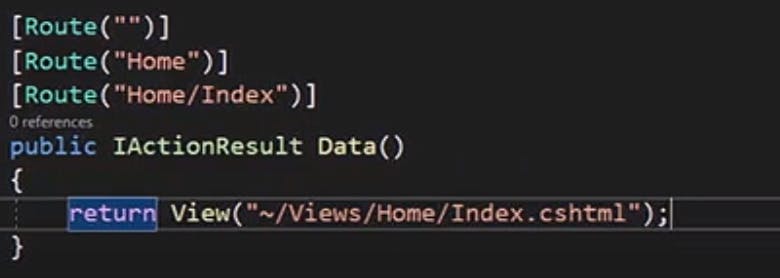
We can we class level routing attribute to remove common routing in methods as
[Route("Home")]
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[Route("Index")] // Matches Home/Index
public IActionResult Index()
{
// Your Index action logic here
return View();
}
[Route("Details/{id:int?}")] // Matches both "Home/Details" and "Home/Details/{id}"
public IActionResult Details(int? id) // Accepts nullable int for id
{
// Your details view logic
var detailsData = GetDetailsData(id); // Handle cases with and without id
return View(detailsData);
}
}